
The first case ( phys) requires a physical device and is therefore not often used. Typically containers can be given their own hardware device (from the host, phys) or can have a virtual device ( veth) that is either put directly on a bridged network device that it shares with the host (uses the same DHCP server and addresses as the host) or put on a bridged network device that is masqueraded to the outside world and that is given an internal subnet.

As a quick overview check out the "Networking Essentials" section below. There is much conflicting documentation due to differing versions. IPv6 support currently (in Stretch, TODO: what about buster?) requires manual configuration.įor a complete manual setup without the convenience of lxc-net, see the networking section below. Since "Debian stretch" there are helper scripts called lxc-net that allow you to set up a simple bridge for your containers, providing a DHCP-and-NATed IPv4 network. Please note that most container templates configure the first interface to use DHCP by default.
#Lxc ssh copy id how to#
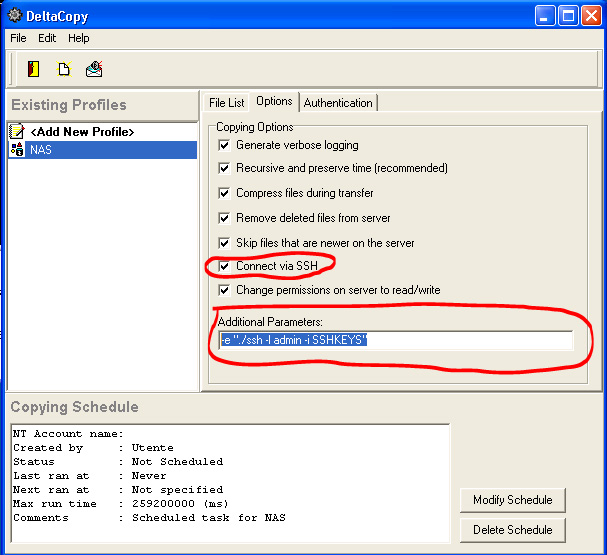
You will probably also have to setup a bridge, firewall and maybe DHCP (see below for details how to do this). If you want to have network in your containers (and you usually do), you will have to either change the global default or configure each individual container. See the upstream documentation for information about the various types of networking available in LXC.ĭebian's packages do not ship any default network setup for containers: (Note: libpam-cgfs is unnecessary if host Linux uses pure CGroup V2.
#Lxc ssh copy id install#
apt-get install lxc libvirt0 libpam-cgfs bridge-utils uidmap.If you want LXC to run unprivileged container(s), the package requirements are slightly different. Typically required packages are lxc, debootstrap and bridge-utils (the latter two are recommended by the lxc package). LXC (upstream) has the following releases: The work to move information about other than stable releases off into its own subpages is in progress. Other Debian/LXC releases are documented in subpages of this document (see the top of this page). The rest of this page will describe LXC in the currently stable Debian release. The 2.1 release, for example, changes the configuration file structure in several ways. When looking for documentation, howtos and tutorials, please check which LXC version they apply to, as things might have changed. Preparing host system WITHOUT Systemd for running LXC.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
